

A researcher is concerned whether, on average, Alzheimer’s caregivers at a particular facility are clinically depressed (as suggested by a mean Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score greater than 25).
An engineer wants to determine if a new type of insulation will reduce the average heating costs of a typical house (which are currently $145 per month).

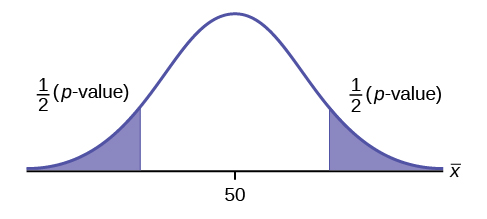
A chemist has invented an additive to car batteries that she thinks will extend the current 36 month average life of a battery.A medical researcher is concerned that a new medicine may change patients’ mean pulse rate (from the “known” mean pulse rate of 82 bpm for individuals in the study population not using the new medicine).A research hypothesis is a “wordy” statement about the question or phenomenon that the researcher is testing. Hypotheses are classified into two types: (1) research hypothesis and (2) statistical hypotheses. This process and the theory underlying statistical hypothesis testing is explained in this module. Probability (Module 12) is used to measure the degree of matching, with sampling variability taken into account. Data is then collected and statistical methods are used to determine whether the observed statistic closely matches the prediction made from the null hypothesis or not. One of these hypotheses (the null) is used to predict the parameter of interest. Statistical hypothesis testing begins by formulating two competing statistical hypotheses from a research hypothesis. Statistical hypothesis testing is key to using the scientific method in many fields of study and, in fact, closely follows the scientific method in concept. If the results of the experiment closely match the predictions, then belief in the hypothesis is gained, though the hypothesis will likely be subjected to further experimentation. If the results of the experiment do not match the predictions, then the hypothesis is rejected and an alternative hypothesis is proposed. Draw a conclusion (from how the observations match the predictions).Use the hypothesis to predict new observations.Formulate a hypothesis to explain the phenomenon.Observe and describe a natural phenomenon.In its simplest form, the scientific method has four steps: 16.1 Confidence Intervals and Precisionġ3.1 Hypothesis Testing & The Scientific Method.15.3 Example Confidence Region Calculations.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
